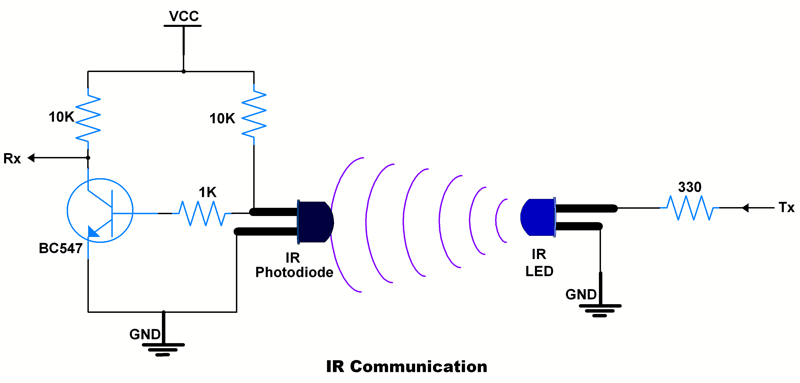
Infrared light-emitting diode is a diode that emits infrared rays, and is usually used in remote controls and other occasions. Commonly used infrared light-emitting diodes are similar in shape to light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and emit infrared light.
Directional Properties
The emission intensity of infrared LEDs varies depending on the emission direction. When the direction angle is zero, its radiation intensity is defined as 100%. When the direction angle is larger, its radiation intensity is relatively reduced. If the emission intensity is half of its direction angle from the optical axis, its value is half of the peak value. This angle is called the direction half-value angle, and the smaller the angle is, the more sensitive the directivity of the device is. Generally, infrared light-emitting diodes are equipped with lenses to make their directivity more sensitive
Distance Characteristic
The radiation intensity of infrared light-emitting diodes varies with the distance on the optical axis and also with the different light-receiving elements. It is the change of the incident light amount of the light-receiving element and the distance from the infrared light-emitting tube that have certain characteristics. Basically, the amount of light is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, and it is related to the different characteristics of the light receiving element.
When emitting infrared rays to control the corresponding controlled device, the controlled distance is proportional to the emission power. In order to increase the control distance of infrared rays, infrared light-emitting diodes work in a pulsed state, because the effective transmission distance of pulsating light (modulated light) is proportional to the peak current of the pulse, and the emission distance of infrared light can be increased by increasing the peak Ip as much as possible. The way to improve Ip is to reduce the pulse duty cycle, that is, to compress the pulse width T. Generally its use frequency is below 300KHz.
Receiving Method
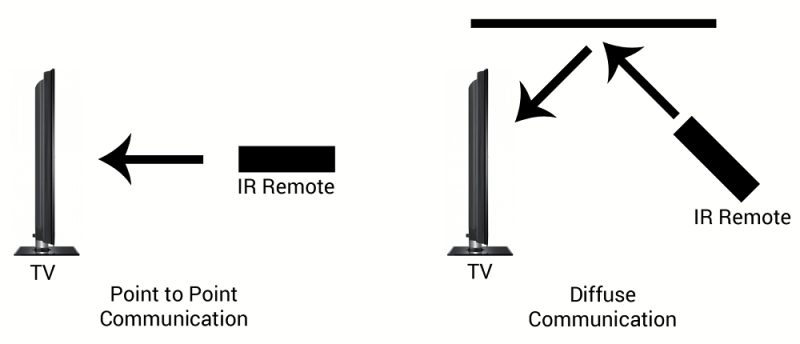
There are two ways to emit and receive infrared rays, one is direct and the other is reflective. The direct type means that the luminous tube and the receiving tube are relatively placed at the two ends of the transmitter and the controlled object, with a certain distance between them; the reflective type means that the luminous tube and the receiving tube are placed side by side, and the receiving tube is always without light at ordinary times, only in the infrared light emitted by the luminous tube. When the light meets the reflector, the receiving tube will only work when it receives the reflected infrared light.