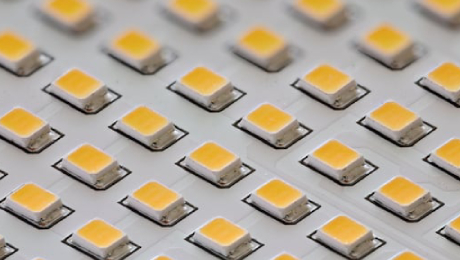
With the rapid development of modern electronic technology, SMD LEDs are a mainstream component used for display and lighting in the current electronic field. They are small in size, low in power consumption, uniform in emission, and have a wide range of applications. They can be used in electronic products, lighting products, traffic signal lights, car lights, and other fields. Next, let’s delve deeper into SMD LEDs. The Basic Principles of SMD LEDs The basic structure of SMD is a substrate sandwiched between a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor. By applying voltage to these two semiconductors, electron hole pairs can be formed within the inclusion layer to emit light. SMD LEDs have high luminous efficiency, and in fact, they have become one of the mainstream products in LED lighting applications. Application characteristics of SMD LEDs Small size: SMD LEDsare small in size and light in weight, generally 20% to 30% smaller than conventional LED lights, making them easy to carry and install. Low power consumption: SMD LEDsnot only have small size, but also have low power consumption, greatly saving electricity and bills. Sharp and Vulnerable: The surface of the SMD is encapsulated in plastic, which has a short service life and durability. Therefore, pay attention to the usage environment and conditions to avoid causing losses. Uniform luminescence: The light output angle of the SMD LED point light source is relatively small, and the radiation direction is relatively concentrated, so the lighting effect will be better when the light is more concentrated. In summary, SMD LEDs are widely used in the electronic field. Their compact size, significant energy-saving effects, and long service life make them an indispensable part of modern electronic technology. But at the same time, we also need to pay attention to protecting the environment, regulating costs, and optimizing design, so that SMD LEDs can play a greater role in the application process.
Category Archives: LED Diode Q&A
Round LEDs and energy-saving lights are both popular lighting devices in the modern lighting field. They have many similarities, both of which are aimed at energy conservation and environmental protection, improving energy utilization efficiency. However, there is still a gap between the two, so which is better and more energy-efficient, Round LEDs or energy-saving lights? Let’s analyze and compare below.
LED display is a high brightness display screen based on LED technology, which is suitable for various indoor and outdoor occasions and has wide applications in information dissemination, advertising dissemination, entertainment display, and other aspects. The following will introduce the functions and characteristics of LED displays.
Photodiode LEDs, also known as Photodiode LEDs, are electronic components that can convert light into electrical energy. Its structure is similar to a regular PN junction diode, but there is a transparent window above the PN junction for receiving optical signals. Photodiode LEDs are widely used in fields such as communication, optoelectronic detection, automatic control, and medical equipment.
Infrared LEDs play a significant role in many fields, using semiconductor technology to convert electrical energy into infrared light energy, with various applications. Below, we will talk about their roles in various fields.
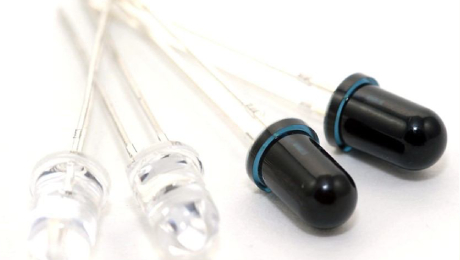
Through hole LEDs is a type of light bead installed through holes on a circuit board, which can be used in various applications such as indicator lights and lighting. Compared to surface mounted SMD light-emitting diodes, it has higher stability and durability.
SMD LED is a surface mounted lamp bead suitable for various electronic circuit applications such as indicator lights, lighting, and displays. In daily use, its wavelength, brightness, appearance, and other parameters have certain classifications.
UV LED is a device that uses UV radiation for sterilization and disinfection. After a certain period of exposure, it can kill bacteria and viruses, and has a good disinfection effect. So what is its disinfection effect? What should I pay attention to when using? Let’s take a look together. The disinfection principle of UV LEDs Firstly, the disinfection principle of UV LEDs is based on the bactericidal effect of UV radiation. UV radiation is a high-energy electromagnetic wave with short wavelengths and strong penetration, which can damage the DNA structure of bacteria and viruses, making them unable to replicate and grow, achieving the effect of sterilization and disinfection. Pay attention to these when using UV LEDs Secondly, there are several points to pay attention to when using UV LEDs. Before use, the surface of the lamp should be cleaned and free from dust and dirt; When using, glasses should be worn to avoid direct exposure of the eyes to UV radiation; Before use, all indoor light sources should be turned off and the indoor color should be kept dark; The irradiation time needs to be determined based on the object and environment, generally ranging from 15 to 30 minutes or even longer; Do not let pets enter during the irradiation process to avoid adverse effects. In addition, UV LEDs are also divided into three wavelengths: UVA, UVB, and UVC. Among them, UV LEDs with UVC wavelength can kill most viruses and bacteria and are the most commonly used disinfection tool. However, it should be noted that UVC UV LEDs can cause damage to the skin and eyes if the exposure time is too long or the exposure distance is not appropriate. In summary, UV LEDs have excellent disinfection effects. When using them, it is necessary to pay attention to disinfecting objects, irradiation time, and not excessively exposing skin to UV LEDs. At the same time, when choosing and purchasing UV LEDs, products with good quality and high safety should be chosen.
With people’s pursuit of green environmental protection and efficient energy conservation, high power LEDs has become a development trend in the lighting industry. What are the characteristics and principles of high power LEDs? Let’s take a look together. Compared to ordinary LED lamps, high power LEDs A high power LED is a semiconductor device that has higher power and light output compared to ordinary LEDs, typically above 1 watt. This also makes it widely used in fields such as lighting, car lights, and signal lights. The working principle of high power LEDs The working principle of high power LEDs are similar to that of ordinary LEDs. When a voltage is applied forward through its two electrodes, a p-n junction is formed in the area where they come into contact. In the p-n junction, electrons and holes recombine, releasing energy and producing photons. The energy and wavelength of such photons depend on the properties of the semiconductor material. The semiconductor materials used in high power LEDs are usually III-V semiconductor materials with a wide bandgap of gallium phosphide and a direct transition to the bandgap. So, what are the differences between high power LEDs and ordinary LEDs? There are two main differences here. Firstly, high power LEDs can withstand higher currents and power, thus generating stronger optical output. Secondly, high-power LEDs typically use multiple light-emitting chips and lenses to achieve higher light output and a wider illumination range. This design can also effectively reduce light attenuation and improve service life. So high power LEDs have the advantages of high efficiency, energy conservation, long lifespan, and environmental protection, and play a significant role in the lighting and electronics industries in daily life.
Introduction UV LEDs are light-emitting diodes that emit ultraviolet light. These devices have a wide range of applications, from disinfecting surfaces to curing UV-sensitive materials. UV LEDs are becoming increasingly popular due to their many benefits, including low power consumption, long lifetime, and compact size. What are UV LEDs used for? UV LEDs are widely used in various applications that involve the generation, detection, and measurement of ultraviolet light. This can range from medical diagnosis to plant health monitoring. UV LEDs are also used for electronic document authentication, and in security and forensic applications. They can be used for disinfection and purification of water, air, and surfaces, as well as for curing of UV-sensitive materials such as adhesives and coatings. UV LEDs also have applications in general lighting, such as for curing nail polish and for blacklight entertainment lighting. UV LEDs are also increasingly being used in UV-C lighting, which is used for disinfection of surfaces, air, and water. These UV-C LEDs emit light at wavelengths of between 200 nm and 280 nm, which is ideal for germicidal irradiation and other such applications. What are the benefits of UV LEDs? UV LEDs have a number of significant benefits over traditional UV light sources. The most notable of these benefits is the low power consumption, which makes them ideal for battery-powered applications. The low power requirements also reduce the thermal load and associated power losses. UV LEDs have a long lifetime and are highly reliable, making them suitable for both commercial and industrial applications. Additionally, UV LEDs are also very compact, making them suitable for use in space-constrained applications. The small size allows for easier integration into existing systems and aids in thermal management, as the small size produces less heat. Another major benefit of UV LEDs is the decreased chance of accidental exposure to the UV light, due to their small size and the lower intensity of the emitted light than traditional UV light sources. What are the challenges of working with UV LEDs? Despite the many benefits, working with UV LEDs can be a challenge due to potential health risks. The UV light emitted from UV LEDs can cause skin and eye damage if not handled properly. Special safety procedures and precautions must be taken when working with UV LEDs, such as the use of UV-protective eyewear and other protective equipment. UV LEDs can also be more susceptible to damage due to the low voltage and current requirements. To minimize the risk of damage, it is important to use a suitable driver circuit that is specifically designed for UV LEDs. Another challenge with UV LEDs is the frequent need for cooling, as the small size of the LEDs generates more heat than traditional UV light sources. How to get started with UV LEDs Due to the potential safety and maintenance risks associated with UV LEDs, it is important to follow best practices and use the right products for the required application. First, the UV wavelength should be selected according to the specific application and the desired power output. It is also important to select a driver circuit that is suitable for the UV LED, as the wrong driver can cause premature failure. For maintaining a safe environment while using UV LEDs, it is important to always follow the safety guidelines and use the necessary protective equipment, such as UV-protective eyewear. It is also important to ensure adequate cooling of the LED to prevent damage and reduce the risk of fire. Conclusion UV LEDs are increasingly popular due to their many benefits, such as low power consumption, long lifetime, and compact size. However, it is important to understand the potential risks when working with them and to use the appropriate protective equipment and driver circuits. By following these tips, it is possible to safely and reliably use UV LEDs in a wide range of applications.
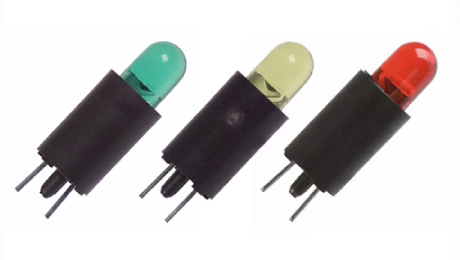
Introduction Circuit board indicator LEDs are an economical and straightforward solution for providing onboard power, control, or activity indications in many different types of electronic systems. These lighting components are used to indicate power status, device on/off conditions, and to show when a particular feature is activated. What are circuit board indicator LEDs? Circuit board indicator LEDs are small, low-power devices typically used to provide visual feedback in electronic devices. They can be used to alert a user that power is present, inform the user when a device is turned on, indicate the operation of certain functions, or even provide light for a display. They come in various colors and sizes, but they typically consist of a base, a light-emitting diode, and a lens. The lens can be clear, diffused, color-tinted, or even reflective, depending on the application. The base can be either soldered directly to the circuit board or mounted on a bracket to produce a remote indicator. How do they work? Circuit board indicator LEDs are typically used in pulsed application, meaning that they turn on and off quickly. This is because the LEDs require current flowing through them in order to produce light, and current dissipates over time unless regularly refreshed. So when a circuit board indicator LED is turned on, it typically draws a certain amount of current, and then automatically shuts off after a certain amount of time. This process can repeat over and over, depending on the application. What are the benefits of using them? The primary benefit of using circuit board indicator LEDs is their low cost, simple design, and ease of use. They are extremely low-power and reliable, and can be used to indicate the status of a device or a function of a device. They also provide a visual display that can provide feedback to users and alert them to changes in the system. How to choose the right one for your project? When choosing the right circuit board indicator LED for your project, there are a few things to consider. First, you need to think about what type of light output you need. Depending on the application, you may need a bright, diffuse light, or a more subtle, dim light. You also need to consider the size, shape and voltage rating. Choose the LED with the correct voltage and current rating for your application. Finally, you need to think about the color you need. Different colors have different meaning and indicate certain functions. Conclusion Using circuit board indicator LEDs is an effective, reliable, and cost effective solution to many situations. They provide visual cues that information can help guide users and show the current status of a device. But when choosing the right LED for your project, you need to consider the size, voltage, color, and brightness of the LED, in order to ensure that it meets your needs.
A 7-segment display is an electronic device that can be used to display numbers and some letters. Different letters/numbers can be represented by connecting different pins on the display to batteries that turn on the LED in parallel. A 7-segment display is an older optoelectronic display device primarily used to display letters and numbers. As the name suggests, these displays consist of seven sections that can be switched on and off to display the desired number or letter. Each part of the display is usually a single LED or liquid crystal. These displays are widely used in electronic counters, digital clocks, home appliance displays, simple calculators, automobiles, and various electronic devices that display digital data. Why are 7-segment displays important? So it’s all about seven-segment displays, types of seven-segment displays, and how to control the position of a seven-segment display, but seven-segment displays are still a great place to start learning about display technology. For this reason, common-anode seven-segment displays are very popular because many logic circuits draw more current than they can source. These displays are not a direct circuit replacement for common anode displays as this is the same as connecting the LEDs in reverse so no light emission will occur. According to the displayed decimal number, the corresponding LED group is forward biased. For example, to display the number 0, we need to light up the segments corresponding to the remaining a, b, c, d, e, f. The numbers 0 to 9 can then be displayed with a seven-segment display. How do 7-segment displays work? Seven segment display interfaced with Arduino is used to easily display 0 to 9 digits. Therefore, these indicators are mostly used in larger electronic projects such as alarm clocks, object counters, timer circuits, digital clocks, etc. A 7-segment display with 7 LEDs arranged to display the numbers 0-9. The 7-segment display is connected to the microcontroller like an LED (ie in series with a current limiting resistor). The only difference is that they have 8 pins instead of 2, since each of the 7 LEDs has its own pin as well as a common cathode or anode pin.
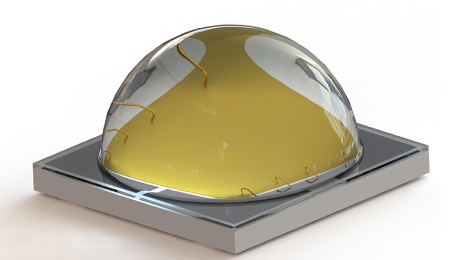
SMD LED (Surface-mounted devices) is a led chip mounted on the surface of a PCB (printed circuit board). Its light-emitting principle is to pass current through compound semiconductors, and through the combination of electrons and holes, the excess energy will be released in the form of light to achieve the effect of light.They are produced using Surface Mount Technology (SMT).
Infrared light-emitting diode is a diode that emits infrared rays, and is usually used in remote controls and other occasions. Commonly used infrared light-emitting diodes are similar in shape to light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and emit infrared light. Directional Properties The emission intensity of infrared LEDs varies depending on the emission direction. When the direction angle is zero, its radiation intensity is defined as 100%. When the direction angle is larger, its radiation intensity is relatively reduced. If the emission intensity is half of its direction angle from the optical axis, its value is half of the peak value. This angle is called the direction half-value angle, and the smaller the angle is, the more sensitive the directivity of the device is. Generally, infrared light-emitting diodes are equipped with lenses to make their directivity more sensitive Distance Characteristic The radiation intensity of infrared light-emitting diodes varies with the distance on the optical axis and also with the different light-receiving elements. It is the change of the incident light amount of the light-receiving element and the distance from the infrared light-emitting tube that have certain characteristics. Basically, the amount of light is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, and it is related to the different characteristics of the light receiving element. When emitting infrared rays to control the corresponding controlled device, the controlled distance is proportional to the emission power. In order to increase the control distance of infrared rays, infrared light-emitting diodes work in a pulsed state, because the effective transmission distance of pulsating light (modulated light) is proportional to the peak current of the pulse, and the emission distance of infrared light can be increased by increasing the peak Ip as much as possible. The way to improve Ip is to reduce the pulse duty cycle, that is, to compress the pulse width T. Generally its use frequency is below 300KHz. Receiving Method There are two ways to emit and receive infrared rays, one is direct and the other is reflective. The direct type means that the luminous tube and the receiving tube are relatively placed at the two ends of the transmitter and the controlled object, with a certain distance between them; the reflective type means that the luminous tube and the receiving tube are placed side by side, and the receiving tube is always without light at ordinary times, only in the infrared light emitted by the luminous tube. When the light meets the reflector, the receiving tube will only work when it receives the reflected infrared light.
High-power LEDs refer to light-emitting diodes with high rated working power. The power of ordinary LEDs is generally 0.05W, and the working current is 20mA, while high-power LEDs can reach 1W, 2W, or even tens of watts, and the working current can range from tens of milliamperes to hundreds of milliamperes. Working Principle Light-emitting diode (LED) is a solid-state device that can convert electrical energy into light energy. Its structure is mainly composed of PN junction chips, electrodes and optical systems. The basic working principle of LED is a process of electro-optic conversion. When a forward bias voltage is applied to both ends of the PN junction, due to the reduction of the PN junction potential barrier, the positive charges in the P region will diffuse to the N region, and the electrons in the N region will also flow to the N region. The P region diffuses, forming a non-equilibrium charge accumulation in the two regions at the same time. Since the minority carriers generated by current injection are relatively unstable, for the PN junction system, the non-equilibrium holes injected into the valence band will recombine with the electrons in the conduction band, and the excess energy will radiate outward in the form of light. The greater the energy difference between electrons and holes, the higher the energy of the resulting photon. If the energy level difference is different, the frequency and wavelength of the light produced will be different, and the color of the corresponding light will be different. Comparison of high power and standard power LED products Simplify the design process The design process required for standard LED arrays is much simpler than that required for high-power technologies due to considerations that greatly simplify thermal management. In our theoretical example, driving a 1W LED requires 350mA, while a standard array of six LEDs requires only 120mA. High power technology requires the use of heat sinks and metal core PCB boards to ensure that high junction temperatures are avoided resulting in loss of efficiency, reduced lifetime or discoloration. Because standard LEDs do not require the use of heat sinks, metal core printed circuit boards (MCPCBs), capacitors or resistors, these LEDs are easier to design, test and manufacture. This simplified process not only saves time and money in the production process, but also speeds up time to market. Cost saving High-power LEDs require thermal management, which greatly increases the cost of the LED. During the design process, the most expensive addition is the heat sink. Heat sinks can be made from a variety of metal materials, from relatively inexpensive aluminum to more expensive materials that conduct electricity better, such as copper and silver. These expensive materials can lead to an increase in the cost of high-power products by US$1 to US$10, which can be avoided by standard LED devices. Likewise, high-power LEDs also require the use of MCPCBs as another passive cooling technique to control junction temperature. Because the MCPCB material has better thermal conductivity, these boards dissipate heat more efficiently than the cheaper FR4 PCBs used by standard LEDs. However, its cost can be as high as 5 times the cost of FR4 PCB. Cost savings of up to 60% can be achieved by using cheaper FR4 PCBs, eliminating the need for expensive heat sinks, and simplifying design considerations. Save space Standard LEDs are often the best choice when the interior space constraints of a device are very large. As mentioned above, high power LEDs require the additional use of heat sinks and overall space-intensive cooling techniques. Its first task is to create more surface area for cooling by convection and radiation. Larger surface area can help reduce heat more effectively, but it also increases the volume of high-power LEDs. This adds design hurdles for smaller spaces and smaller products. Standard LED arrays typically do not require the space-consuming drivers, capacitors, and resistors required for high-power LEDs, resulting in space savings of up to 50%. For space-constrained applications, standard LED arrays can provide the same brightness as high-power LEDs while saving space.